Air Conditioning Capacitor: The Unsung Hero of Your HVAC System
Introduction
When it comes to staying comfortable during scorching summers or chilly winters, air conditioning systems have become a necessity. These systems rely on various components to function effectively, and one of the key players in ensuring smooth operation is the air conditioning capacitor. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the air conditioning capacitor, how it works, common issues, and the steps to maintain it properly.
1. Understanding the Role of an Air Conditioning Capacitor
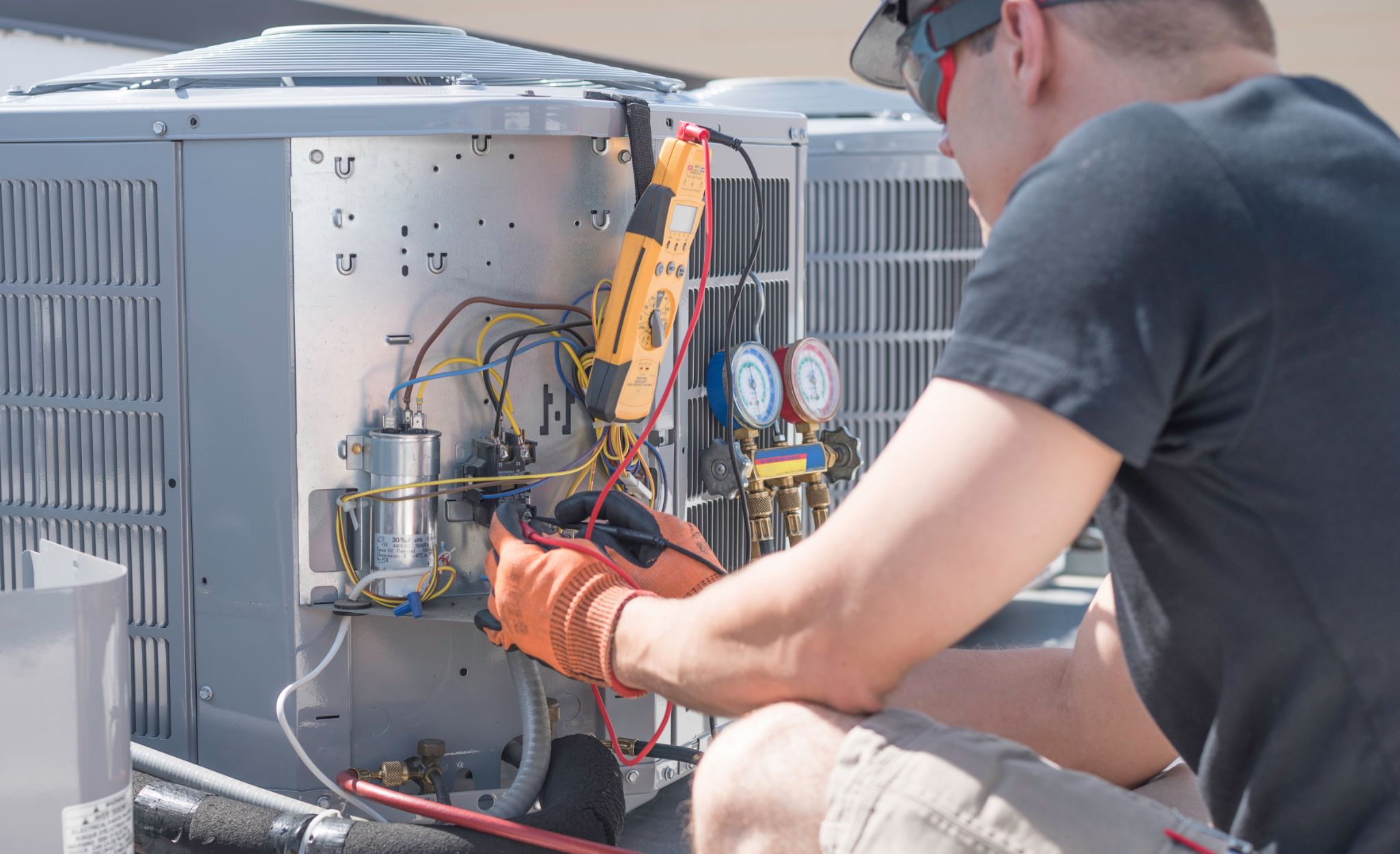
To comprehend the significance of an air conditioning capacitor, we first need to understand its role in the system. The capacitor serves as a temporary energy storage device that provides the initial jolt of power to start the compressor and the fan motor. Without this boost, the HVAC system would struggle to begin its cooling or heating process efficiently.
2. How Does an Air Conditioning Capacitor Work?
An air conditioning capacitor operates on the principle of electrical potential energy. It consists of two metal plates separated by an insulating material known as a dielectric. When voltage is applied, an electric field is formed, causing an accumulation of charges on each plate. As the potential difference increases, the capacitor stores energy until it reaches its threshold. Once the HVAC system signals for the compressor or fan motor to start, the capacitor discharges the stored energy, providing the necessary kickstart.
3. Types of Air Conditioning Capacitors
There are primarily two types of capacitors used in air conditioning systems: start capacitors and run capacitors. Start capacitors deliver the extra torque required during system startup and are designed to disconnect from the circuit once the motor reaches its operating speed. On the other hand, run capacitors remain continuously connected to provide a phase-shifted current, which helps the motor maintain a consistent speed during operation.
3.1 Start Capacitors
Start capacitors are usually larger in size and possess a higher capacitance value. They deliver the extra torque required during the motor’s startup phase, enabling it to overcome inertia and start running smoothly.
3.2 Run Capacitors
Run capacitors are designed for continuous operation, supporting the motor during its entire runtime. They help maintain a consistent speed and enhance the overall efficiency of the HVAC system.
4. Common Issues with Air Conditioning Capacitors
Like any other component in an HVAC system, air conditioning capacitors are susceptible to wear and tear. Some common issues include:
4.1 Capacitor Failure
Over time, capacitors can wear out due to constant charging and discharging cycles. A failed capacitor can lead to the HVAC system’s failure to start or inefficient operation.
4.2 Capacitor Leaks
Capacitors are housed in metal cases, and over time, these cases may develop cracks or leaks, compromising the capacitor’s performance.
4.3 Capacitor Bulging
Bulging capacitors are a result of internal pressure build-up due to excessive heat or electrical stress. A bulging capacitor needs immediate replacement to avoid further damage.
5. Maintaining Your Air Conditioning Capacitor
To ensure your HVAC system operates optimally, regular maintenance of the air conditioning capacitor is crucial.
5.1 Regular Inspection
Schedule periodic inspections by a qualified technician to check for any signs of wear or damage to the capacitor.
5.2 Cleaning
Keep the area around the capacitor clean and free from debris to prevent overheating.
5.3 Capacitor Testing
Technicians can conduct capacitor tests to assess its health and identify any potential issues before they escalate.
6. Conclusion
The air conditioning capacitor may be a small and often overlooked component of your HVAC system, but it plays a vital role in keeping your home comfortable. Understanding its importance, how it works, and how to maintain it can extend the lifespan of your HVAC system and ensure optimal performance.





0 comments
Write a comment